The Digital Renaissance: Why Traditional Search Engine Optimization Is Obsolete
The rules of digital discovery have fundamentally changed. For years, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) was the undisputed king, dictating how brands attracted traffic by meticulously chasing keywords, building backlink profiles, and optimizing page structure. However, the rise of powerful Generative AI systems has rendered much of traditional SEO obsolete for most websites. What was once a gradual evolution is now an overnight revolution, fundamentally reshaping the content landscape.
The truth is, while many marketers are still focused on securing a high position in the “ten blue search results,” user behavior has shifted dramatically. Users no longer click to find answers; they ask for them. Whether through ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, or Google’s own AI Overviews, the direct answer is now the primary deliverable. This shift has decimated click-through rates (CTRs) for organic results and opened a new frontier: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
GEO is not a mere tactic; it is the complete future of online visibility. It represents the crucial transition from optimizing for human clicks to optimizing for AI citation. The brands that master this new methodology first will not just survive; they will dominate their markets, leaving competitors who cling to outdated SEO tactics far behind.
The Irreversible Decline of Traditional SEO
The notion that SEO is “dead” is deliberately provocative, but for independent websites relying on traffic from standard organic search listings, the reality is brutal. SEO is not changing; for most, it has already collapsed under the weight of three irreversible trends.
1. Direct Answers Decimate Click-Through Rates
The primary function of AI chatbots and generative features in search is to provide instant, summarized, and sourced answers directly on the platform.
- AI Overviews and Featured Snippets: Google now places AI-generated summaries, knowledge panels, and featured snippets above all standard organic listings. Users receive their answer without ever scrolling to the traditional organic results.
- Conversational Search: Platforms like Perplexity and various LLMs (Large Language Models) deliver instant answers with sources. A user with a simple question has no reason to click through ten separate search results.
This behavioral shift means that even ranking number one for a valuable keyword may now yield only a fraction of the traffic it did three years ago. The value of the click itself has been diluted by the generative summary. For a comprehensive study on this decline, explore the latest Search Engine Land reports on zero-click searches.
2. Search Result Pages Are Beyond Saturation
Modern Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) are an overcrowded battlefield. By the time a user reaches the “first organic result,” they have already scrolled past an imposing wall of high-friction content:
- Commercial Overload: The top of the page is dominated by highly visible paid advertisements (PPC).
- Rich Features: Below the ads sit the AI Overviews, followed by featured snippets, local packs (for geo-specific queries), and often several social media and video results.
For most users, navigating past this dense array of featured content to reach the generic blue results is simply too much effort. The visible “real estate” for traditional organic rankings has effectively been pushed below the fold, rendering even high rankings increasingly ineffective for traffic generation.
3. The Trust Barrier: Google’s Brand Bias
A less-discussed but equally devastating trend for independent publishers is Google’s increasing bias toward established, large-scale entities. Major algorithm updates over the past few years have consistently rewarded huge platforms over smaller, high-quality, specialized sites.
- Domain Trust and Authority: Google’s algorithms now prioritize domain authority and brand recognition as proxies for quality, even when a smaller site’s content is more detailed or specialized.
- The Rise of Aggregators: Websites like Reddit, Quora, and Wikipedia—which aggregate user-generated content or serve as established reference sources—have seen their search presence explode. This is not solely due to superior content but because Google’s systems have learned to trust their established brand identity. Independent websites, conversely, have reported traffic drops exceeding 60%, showing that the old tactics of superior user experience and granular optimization are no longer enough to overcome the inherent brand bias of the algorithms.
If you are still dedicating the majority of your budget to keyword density and non-strategic backlinks, you are betting your business on a strategy that is actively being penalized and diminished by the very engines you seek to serve.
Understanding Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
GEO is the strategic practice of creating content specifically designed for consumption, reference, and citation by Large Language Models and Generative AI engines.
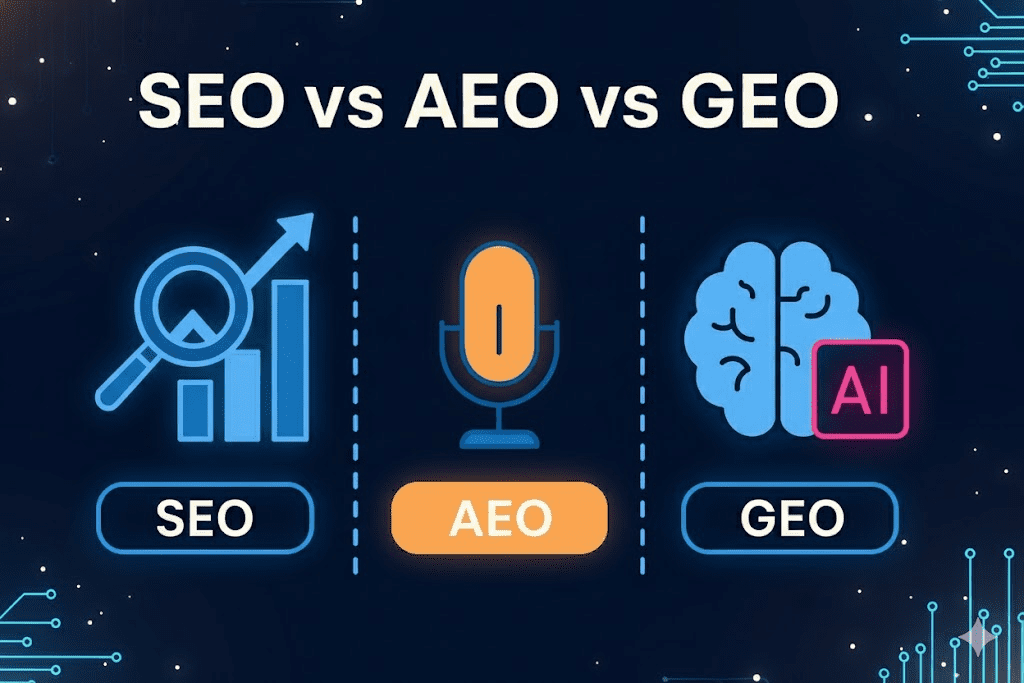
GEO vs. SEO vs. AEO: A Critical Distinction
To grasp the future, one must distinguish GEO from its predecessors:
| Strategy | Primary Goal | Target Platforms | Core Tactic |
| Traditional SEO | Get clicked by human users. | Google, Bing (Organic Listings). | Keyword density, referral volume, meta tags. |
| Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) | Get selected for a visible answer box. | Google Featured Snippets, Voice Search. | Q&A format, structured data (Schema). |
| Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) | Get cited and quoted within AI-generated answers. | ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, AI Overviews. | Machine readability, entity authority, citation formatting. |
Where SEO focused on discovery and AEO focused on selection, GEO focuses on authority and citation. Your content must become the most reliable, structured, and definitive source that an AI system reaches for when synthesizing an answer for a user.
Why Citation is the New Click
When ChatGPT or an AI Overview cites your website as the source for an answer, it delivers several high-value outcomes far superior to a single click:
- Instant Credibility: The citation immediately establishes your brand as an expert in the user’s mind and, more importantly, in the AI’s knowledge graph.
- Massive Exposure: The answer is exposed to potentially millions of users who are interacting directly with the AI, bypassing the competitive SERP entirely.
- Algorithmic Trust: Every citation reinforces your site’s topical authority with the AI, making it more likely to be cited in future, related queries. This cumulative trust is the ultimate source of long-term visibility. For insights into how AI models determine source authority, refer to published material on AI knowledge graph construction.
This is a fundamental shift in mindset: Stop playing the click-rate game and start playing the citation-rate game.
The Five-Step Blueprint for GEO Content Domination
Mastering GEO requires a methodical approach that prioritizes structure, technical implementation, and strategic intent. This blueprint outlines the exact steps used to create content that AI systems consistently trust and reference.
Step 1: Structure for Machine Readability
AI crawlers and LLMs process information based on patterns and hierarchical structures, not narrative flow. Your content must be organized as a queryable database rather than a traditional narrative essay.
- Micro-Content Segmentation: Use short paragraphs, keeping sentences concise (ideally under 20 words). This facilitates easy extraction of key facts.
- Clear Hierarchy: Employ distinct and logical headings (
H1,H2,H3) to signal the topic and sub-topics. - Format for Extraction: Break down complex information using clear bullet points and numbered lists. These formats are easily pulled and synthesized into AI-generated summaries.
- Consistent Terminology: Use consistent language and terminology across all related content. This helps the AI connect ideas and build a robust profile of your expertise. For more detail on creating scannable web content, refer to the Nielsen Norman Group guidelines on web design.
Step 2: Implement Advanced Structured Data Markup
Structured data is the technical language that explicitly tells AI systems what your content is about and what kind of information it contains. This is mandatory for GEO success.
- Schema Markup: Implement relevant Schema markups:
- Use FAQPage Schema for content structured around questions and answers.
- Use HowTo Schema for instructional or step-by-step guides.
- Use Article Schema for blog posts and news content.
- LLMS.TXT File: This is a crucial, emerging technical element. Similar to
robots.txt, the LLMS.TXT file is added to your website’s root directory to specifically instruct AI crawlers (the LLM’s own crawlers, separate from Google’s) on what content to prioritize, what to ignore, and what is specifically authorized for citation. Creating this roadmap ensures AI systems find your best content first.
Step 3: Focus on Entity Recognition and Topical Authority
The era of chasing singular, high-volume keywords is over. AI systems excel at understanding entities (people, places, concepts, organizations) and topical authority (comprehensive expertise across a subject).
- Become the Definitive Source: Instead of just writing one blog post on a topic, create a cluster of inter-related articles covering every facet of a core subject. This signals to the AI that you are the authoritative expert, not just one of many commentators.
- Internal Referencing: Refer related articles together using descriptive anchor text. This builds a robust internal web that helps the AI map your expertise and the relationships between your content entities.
- Reference Authoritative Sources: Reference out to other high-authority sources in your industry to validate your claims and demonstrate that your content exists within a recognized ecosystem of expertise.
Step 4: Optimize for Citation Formats
Not all content is cited equally. You must deliberately create sections of your content that are formatted in ways that AI naturally extracts and quotes as factual statements.
- Factual Claims and Statistics: Make specific, bold, and verifiable claims, immediately followed by supporting data. For example: “The average customer acquisition cost in the SaaS industry increased by 15% this year [Source].” These concise, factual snippets are easily isolated and referenced.
- Clear Definitions: Provide crystal-clear, bolded definitions and explanations for complex industry terminology. AI frequently uses these to populate definitional answers.
- Step-by-Step Processes: Use numbered lists and concise language to outline processes or instructions. AI often quotes these directly when asked “How to…” questions.
Step 5: Iterative Testing and AI Feedback
GEO is not static. You must continuously audit your work using the very tools you are trying to optimize for.
- Content Audit: Review your existing content, looking through the lens of GEO. Are the paragraphs too long? Is the structure clear? Are the claims citable?
- Targeted Content Creation: Select one core topic and create a new, perfectly structured piece of content using all the GEO principles. Make it the most definitive, concise resource on that specific subject available online.
- Test with LLMs: Actively query ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity about your chosen topic. See if your content is cited. If it is not, analyze the generated answer to understand which source the AI did use, and then iterate on your content to make it demonstrably superior in structure and authority. This iterative process of refinement based on direct AI feedback is the core of effective GEO. For advanced guidance on testing, consider this resource on advanced AI content testing methodologies.
The Actionable GEO Implementation Strategy
The window of opportunity for establishing GEO authority is open now, but it is narrowing rapidly. While competitors are stuck optimizing for a declining search environment, those who act quickly can dominate the AI knowledge graph with low initial competition.

Immediate Action Plan
- Audit and Repurpose: Select your three most important articles. Immediately restructure them according to Step 1 (Machine Readability).
- Schema Implementation: Implement the most relevant Schema markup (FAQ, HowTo, Article) across your content pages.
- The LLMS.TXT Advantage: Create and deploy a basic LLMS.TXT file to guide AI crawlers toward your highest-authority content assets.
- Create Your Pillar: Commit to producing one comprehensive, GEO-perfect pillar page on your most valuable industry topic. Ensure it contains citable definitions, statistics, and a logical hierarchy.
- Commitment to the Shift: Accept that this is a long-term strategic shift. GEO is not a quick fix; it is the new foundation for content creation and distribution.
The biggest fortunes in marketing are made during transitions. This is the biggest transition since the creation of the commercial internet. Waiting for proof will ensure you are left playing catch-up for years to come.
Conclusion
The era of traditional SEO, defined by the chase for organic clicks, is over for the majority of businesses. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents the necessary strategic pivot, shifting the goal from securing a high rank to earning a high citation rate within generative AI systems. By meticulously structuring content for machine readability, implementing advanced Schema markup, focusing on entity-level authority, and continually testing content against the leading LLMs, brands can secure their position as the trusted source in the emerging AI knowledge graph. This is not a future possibility; it is the present reality. Those who embrace the GEO blueprint now will solidify their expertise, drive unprecedented exposure, and secure long-term market dominance while their competitors struggle with the rapidly diminishing returns of obsolete tactics.

