Email marketing remains one of the most potent and direct channels for both brand building and high-value business-to-business (B2B) acquisition. While the landscape is constantly evolving with new platforms and technologies, the fundamental principles of success—precision, personalization, and high-quality data—have only become more critical. This comprehensive guide details the essential strategies, technical tools, and data practices necessary to execute effective email campaigns, from fully automated consumer sequences to highly bespoke outreach for senior executives.
I. The Dual Pillars of Email Campaign Strategy: Automation vs. Bespoke Outreach
The world of professional email marketing can be broadly categorized into two strategic approaches, each serving a distinct purpose and audience. Understanding this delineation is the first step toward effective execution.
A. Email Automation Campaigns: Scale, Efficiency, and Behavioral Triggers
Email automation refers to the use of specialized software platforms to send pre-written, highly personalized messages triggered by a recipient’s actions or a set schedule. These are primarily utilized for direct-to-consumer (D2C) or high-volume B2B lead nurturing where the goal is scale and efficiency.

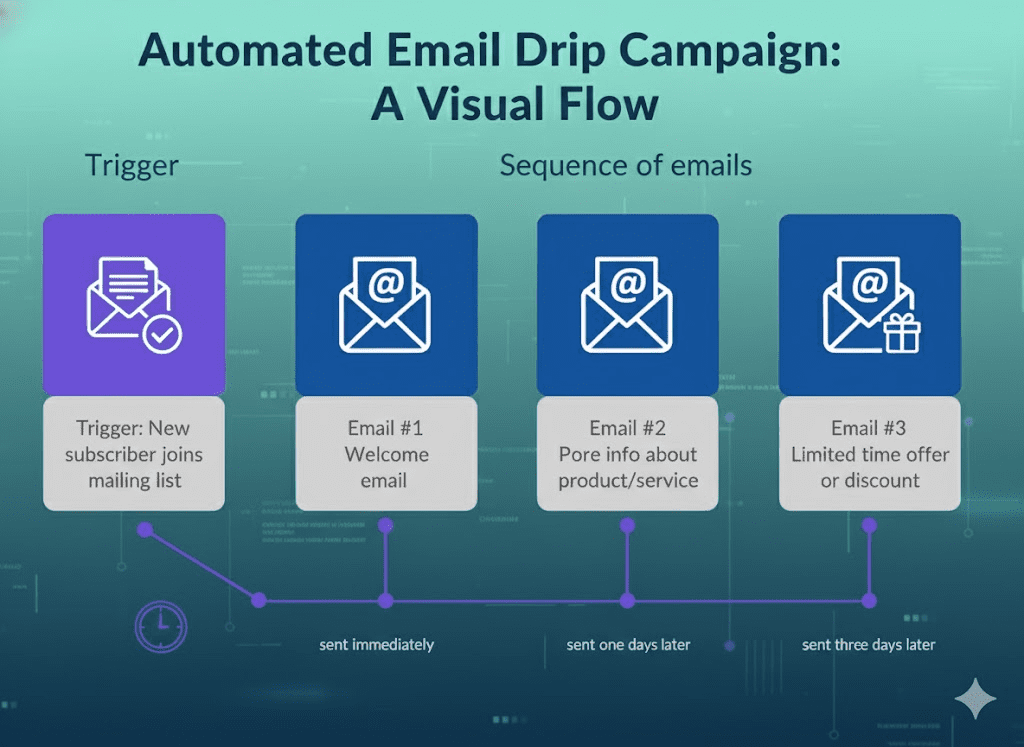
1. Drip Campaigns: The Foundational Sequence
A drip campaign is an automated set of emails, typically a small series, sent at predetermined intervals to a specific segment of subscribers. They are linear and time-bound. A classic example is a welcome series for a new website subscriber. The recipient signs up, receives Email 1 immediately, Email 2 three days later, and Email 3 one week later. The sequence is fixed, regardless of the recipient’s immediate engagement. Drip campaigns excel at:
- Onboarding: Introducing new users to a product or service.
- Education: Delivering scheduled content (e.g., a “seven-day course” on a topic).
- Nurturing: Gently keeping the brand top-of-mind over a longer period.
2. Full-Fledged Email Automation Workflows
Modern email automation platforms, such as Klaviyo (often pronounced “Clavio” by users) or other industry-leading marketing automation suites like HubSpot, Marketo, or ActiveCampaign, offer a far more dynamic and sophisticated approach. These campaigns are built on complex ‘if/then/else’ logic and are entirely behavior-driven.
- Trigger-Based Sending: An email is sent only when a user performs a specific action. Examples include:
- Cart Abandonment: User adds an item to a shopping cart but leaves the website.
- Browse Abandonment: User views a high-value product page multiple times but doesn’t add to the cart.
- Post-Purchase: An email is sent seven days after a purchase to request a review or offer a complementary product (cross-sell/upsell).
- Dynamic Content: The content within the email template changes based on the recipient’s data. For a browse abandonment email, the email is dynamically populated with the exact product the user was looking at.
- Branching Workflows: Based on the recipient’s response to the first email (e.g., Did they click? Did they open?), the platform will send a different, tailored follow-up. This creates a hyper-personalized journey at scale, mimicking a one-on-one conversation without human input.
While these tools offer immense power, they often come with a moderate to steep learning curve initially. Setting up the necessary integrations, defining the customer segments, and mapping out the logical workflows requires a significant investment of time and expertise. However, once established, the return on investment (ROI) through improved conversion rates and efficiency is substantial.
B. Bespoke Email Campaigns: Precision for High-Value B2B Acquisition
In the corporate world, particularly for delegates acquisition for high-end events, securing a corporate round-table attendance, or pitching a high-ticket service to a major enterprise, the automated approach often falls short. Senior executives (CXOs, VPs, Managing Directors, Chairmen) receive an overwhelming volume of communications. Automated, generic emails, even with a high degree of personalization, can be easily flagged as sales spam or simply ignored.
This is where the bespoke, manual email campaign becomes the most effective weapon. This strategy is not about high volume per hour, but about high quality and hyper-relevance per contact.
- Human-Centric Execution: This approach involves drafting and sending emails one-by-one, or in small, controlled batches, often bypassing the large-scale automation platforms to ensure maximum inbox deliverability and a more personal feel. The process typically involves:
- Maintaining a highly curated list in a format like Microsoft Excel or a lightweight Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system.
- Manually copying and pasting the email address into the ‘To’ field.
- Customizing the subject line and the opening sentence based on recent company news, an article the executive wrote, or a shared connection.
- Hitting ‘Send’ with the confidence that the message is landing in a highly-vetted inbox.
- The Power of the Human Touch: The bespoke campaign is fundamentally a delicate acquisition strategy. It is highly unlikely that a cold automated email will bypass the sophisticated spam filters of a blue-chip company’s CEO—unless that CEO has willingly subscribed via a website landing page. The goal of bespoke outreach is to craft a message so concise, relevant, and human that it warrants a senior person’s attention for a few critical seconds.
II. The Indispensable Foundation: Data Quality and Targeting
No matter the campaign type, the quality and precision of the data list are the absolute determinant of success. An exquisitely crafted email sent to the wrong person or an invalid address is wasted effort.
A. Defining the Ideal Target Audience (ITA)
In B2B marketing, the target list must be highly granular and targeted. This involves moving beyond simple industry and geography to detailed firmographics and technographics.
- Key Firmographic Data Points:
- Company Size: Revenue, employee count (often sorted to target mid-market or Fortune 500 only).
- Industry: Specific vertical (e.g., FinTech, SaaS, Healthcare IT).
- Location: Geographic focus (e.g., London, APAC region, North America).
- Crucial Contactographic Data:
- Job Title/Seniority: Are you targeting CXOs, VPs, Directors, or Managers? Specific titles like Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) or Managing Director are key for high-value outreach.
- Direct Email Address: The single most valuable piece of data. Generic addresses like
info@,contactus@, orhello@are often intercepted by a receptionist or a departmental inbox, leading to deletion or a dead end. The goal is the senior executive’s direct, personal corporate inbox.
B. Data Acquisition: Building a Clean, Compliant List
Acquiring the right data is a significant challenge, especially in the post-GDPR world. The focus must always be on quality over sheer volume. Sending 50 highly targeted, correct emails is infinitely more effective than sending 5,000 to generic, unverified addresses that are likely to bounce or be flagged as spam.
1. Sourcing Data
While businesses may buy highly-vetted data lists from reputable, GDPR-compliant data providers (vendors) like ZoomInfo or Cognism, which can often be sorted by company size, location, and seniority, internal generation remains a vital component.

2. The Challenge of Finding Direct Corporate Emails
In the past, services that would pull email addresses from LinkedIn were prevalent, leading to massive spam issues. This era, preceding the full effect of regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), led to major privacy changes. LinkedIn and other platforms have since tightened their privacy settings, making personal email addresses visible only upon explicit sharing or connection.
- Guessing and Permutating: A common practice is to use educated guesses based on known company email formats. These often include:
firstname.lastname@company.comfirstinitiallastname@company.comfirstname@company.cominitial.lastname@company.com
jane12.doe@company.com) to deter simple guessing. - Verification and Cross-Referencing: Tools like Hunter.io or other email finders/verifiers can help confirm the likely format and check if an address exists.
- Leveraging AI for Clues: Platforms like Perplexity can be used to search for common email formats used by companies in a specific sector, though this should only provide a starting point for further manual verification.
C. The BCC Delivery Optimization Trick
A clever tactic to maximize the chance of delivery when unsure of the exact email format involves the Blind Carbon Copy (BCC) field.
The process works as follows:
- Identify the Most Likely Email: Based on your research (e.g.,
john.doe@company.com), place the single most probable email address into the ‘To’ field. This address will be visible to the recipient. - Use the BCC Field for Guesses: Place a selection of other plausible variations (e.g.,
j.doe@company.com,john.d@company.com,johndoe@company.com) into the ‘BCC’ field. These addresses are hidden from all recipients. - The Result: If the address in the ‘To’ field bounces (is incorrect), but one of the addresses in the ‘BCC’ field is correct, the recipient will still receive the email. Critically, the email they receive will appear as if it was sent only to the visible ‘To’ address, maintaining the privacy of your other speculative addresses and preserving the highly personalized, one-on-one appearance of your bespoke outreach. This increases your deliverability rate without sacrificing personalization.
D. Data Compliance: Navigating GDPR and PECR
Working with any personal data, even corporate email addresses, requires strict adherence to regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Privacy and Electronic Communications Regulations (PECR).
- Lawful Basis: For B2B email marketing, the most common legal basis for cold outreach is “Legitimate Interest,” not explicit consent (which is typically required for B2C). Legitimate Interest means the company has a valid business purpose (e.g., promoting a relevant product) that is balanced against the recipient’s privacy rights, and the recipient would reasonably expect to receive this communication.
- Transparency and Opt-Out: Regardless of the lawful basis, every marketing email must include clear information on how the recipient’s data was obtained and a simple, explicit mechanism to opt-out (unsubscribe) from future communications. Failure to include this can result in heavy fines.
- Data Accuracy and Retention: The GDPR requires data to be kept accurate and not held longer than necessary. Regular list cleaning to remove bounced or inactive contacts is not just a best practice for deliverability; it is a legal requirement for compliance.

III. The Art and Science of Crafting High-Converting Email Copy
With the right data and the correct strategic approach, the next challenge is the message itself. High-converting email copy, especially for senior executives, must be the antithesis of generic marketing prose.
A. The Bespoke Copy Imperative: Humanizing the Message
The core mistake marketers make in high-value outreach is over-automating the copy. To land a meeting with a senior executive, the email must sound as if it was written by one human to another. It must be humanized.
- Avoid the ‘AI Giveaways’: Many initial drafts created by large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Gemini, or other AI assistants, contain telltale signs of automation:
- Overly Formal or Flowery Language: “It is imperative that we consider…” or “In light of this information…”
- Generic Structure: Too many bullet points, perfect formatting, and a tone that is too “clean” or “professional.”
- Lack of Personality: No small, human element of humor, personal observation, or unique phrasing.
- The Humanization Workflow:
- Start with the Human Draft: The most effective method is to write the first draft yourself, as a human being would, focused on a concise, value-driven pitch.
- Refine with AI: Use AI to polish the draft. You can use platforms like QuillBot’s Humanize AI or Ahrefs’ Paraphrasing Tool to:
- Shorten and Clarify: Ask the AI to take the core message and make it shorter and clearer.
- Refine the Tone: Instruct the AI to modify the language to be “professional but friendly,” “corporate with a pinch of humor,” or “direct and concise.”
- Generate Alternatives: Use the AI to generate multiple (e.g., 10-20) variations of the subject line and the first paragraph.
- Final Human Edit: The final, critical step is to review the AI-generated options and select the one that feels the most natural, then tweak it further to inject genuine human voice and a specific, bespoke reference to the recipient’s company or title.
B. Key Copy Elements for Conversion
Every element of the email must be engineered to push the recipient toward the single, desired outcome.
- The Subject Line: This is the gatekeeper. It must be enticing enough to warrant an open but not spammy. Effective subject lines are highly personalized, state a clear value proposition, or create curiosity. Examples: “Quick question on your Q3 growth” or “Idea for [Company Name]’s delegate acquisition.”
- The Opening Hook: The first sentence must justify the email. It should reference a point of connection: “I saw your keynote at [Event Name],” or “Your recent press release on [Topic] caught my eye.”
- Value Proposition: The core of the message must be the recipient’s benefit, not the sender’s product features. The message must answer the recipient’s silent question: “What’s in it for me?” Focus on solving a specific, known pain point for a person in their role (e.g., “We help VPs of Sales reduce their lead conversion time by 15%”).
- The Single Call-to-Action (CTA): For high-value, bespoke outreach, the CTA must be incredibly simple and low-friction. The goal is often just to get a conversation started, not to force a sale. A polite, open-ended question works best: “Would you be open to a 15-minute call next week?” or “Is this a challenge that’s on your radar?”
IV. Measuring, Iterating, and Scaling Success
The process of email marketing, whether automated or bespoke, is a continuous loop of testing and refinement.
A. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
For all campaigns, performance must be tracked meticulously.
- Open Rate: The percentage of recipients who open the email. This is directly influenced by the subject line and sender reputation/deliverability.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of recipients who click a link inside the email. This measures the effectiveness of the email body copy and CTA.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of recipients who complete the desired action (e.g., book a meeting, make a purchase, download a resource).
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of emails that could not be delivered (hard bounces for invalid addresses, soft bounces for temporary issues). A high bounce rate severely damages a sender’s reputation and deliverability. This is the clearest indicator of poor data quality.
- Unsubscribe Rate: The percentage of recipients who opt-out. A high rate suggests poor targeting or a misalignment between the email content and the audience’s expectation.
B. The Importance of Data Hygiene
Regularly cleaning and updating the email list is the single most effective action to protect deliverability and reputation.
- Remove Bounces: Immediately remove any addresses that result in a hard bounce. Continuing to send to these addresses tells Internet Service Providers (ISPs) that the sender is either spamming or using outdated data.
- Re-engagement Campaigns: Periodically run campaigns to re-engage subscribers who haven’t opened or clicked an email in a long time. If they remain inactive, it is best to remove them from the active mailing list to maintain a high level of engagement overall. A smaller, highly-engaged list is always more valuable than a large, disengaged one.
V. Conclusion: Precision as the Ultimate Strategy
The modern email marketing landscape is defined by a dichotomy: the highly scalable, behavior-triggered automation of D2C and mass-market campaigns, and the hyper-targeted, human-driven approach necessary for high-value B2B acquisition. While the former relies on complex software ecosystems like Klaviyo and dynamic content, the latter hinges on meticulous data vetting, humanized copy, and personal, one-to-one outreach.
The central, unifying principle across all effective email strategies is the quality and precision of the data. In a world saturated with generic digital noise, success is not found in sending the most emails, but in sending the right email, to the right senior executive, at the right company, with the right direct email address. This focus on quality information—accurate names, precise corporate contact details, and highly-targeted audience lists—is the key differentiator. By prioritizing a well-vetted database, mastering the art of bespoke, humanized communication, and diligently tracking performance, any organization can transform its email channel from a mere broadcast tool into a powerful engine for high-conversion delegate and enterprise acquisition.

