The integration of artificial intelligence technologies into global business is rapidly gaining momentum, and the field of Human Resources (HR) is at the forefront of this transformation. According to the research firm Grand View Research, the global HR Tech market size was valued at over $24 billion USD recently and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 10% through 2030.
More than half of global employers have identified the automation of personnel processes as a primary trend. Furthermore, a study by the consulting group McKinsey & Company reveals that nearly 76% of HR leaders believe AI will be critical to their organization’s future success, with many already implementing GenAI solutions.

In this article, we will analyze how AI helps to strengthen the competencies of HR specialists worldwide and which tasks can be automated using neural networks today. We will also look at a step-by-step plan for implementation, review popular global AI tools, and study real cases of multinational companies that have achieved significant optimization. Finally, we’ll explore expert forecasts for the future of HR technology.
Why Does the HR Department Need Artificial Intelligence?
AI is not designed to replace the HR specialist. Its main task is to take over routine, repetitive, and time-consuming operations, freeing up professionals for strategic work, relationship building, and decisions that require emotional intelligence. The main areas of application include:
1. Recruitment and Hiring
- Resume Screening: Modern AI systems use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze resumes. They don’t just look for keywords; they understand context, recognize synonyms, and associate skills with achievements. For example, if a candidate writes about “optimizing a sales funnel,” the system automatically detects data skills and business acumen, regardless of the specific terminology used.
- AI Bots for Pre-selection: Chatbots and voice robots answer candidates’ questions 24/7, conduct initial interviews, collect data on experience and motivation, filter candidates by basic criteria, and even schedule meetings for successful applicants. This drastically reduces response times—often referred to as “Time to Hire”—and improves the candidate experience.
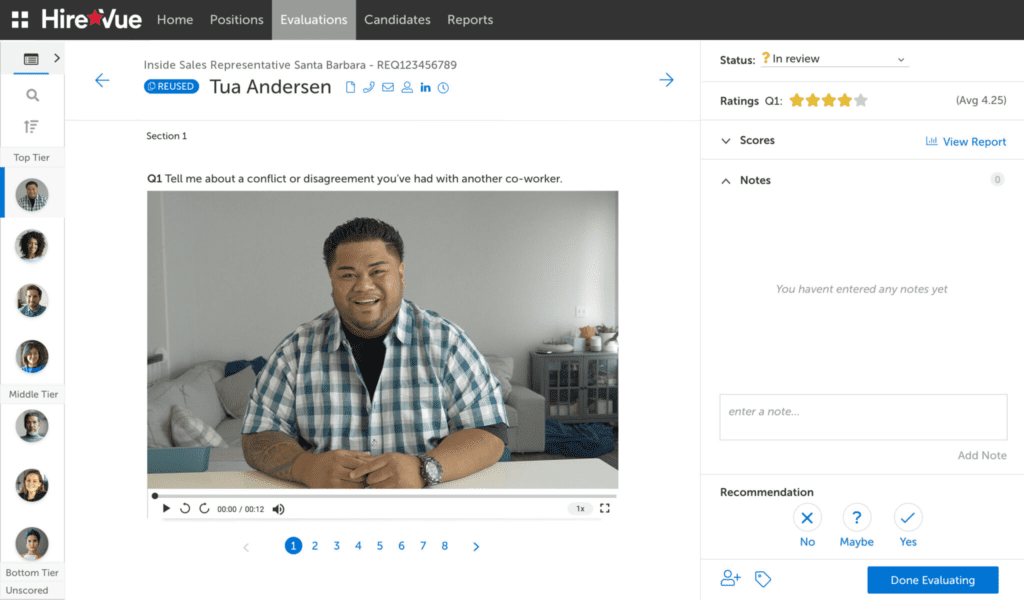
- Video Interview Analysis: Services like HireVue analyze not only speech but also facial expressions, gestures, intonation, and pauses. This allows recruiters to assess soft skills like stress resistance, confidence, and focus objectively before a personal meeting.
- Database Updates: AI can automatically contact job seekers in your Applicant Tracking System (ATS) to clarify their current employment status and interest in new jobs, keeping the candidate database fresh and avoiding “zombie” data without manual recruiter involvement.
- HR Records Automation: AI can generate employment contracts, offer letters, and policy documents by adhering to corporate standards and local labor laws, creating drafts that only need a final check and signature.
2. Staff Management and Retention
- Productivity Analysis: Neural networks comprehensively assess employee effectiveness by analyzing communication patterns, KPI achievement, and activity dynamics during the day. This can uncover hidden issues, such as how multitasking or excessive meetings might be reducing a specific person’s productivity.
- Monitoring Engagement and Burnout: By analyzing the sentiment of messages in corporate communication platforms (like Slack or Microsoft Teams) and changes in work behavior (start/end times, break frequency), AI can detect early signs of burnout. For instance, it can flag if an employee constantly shifts deadlines or expresses negativity in team chats.
- Feedback Analysis: Processing open comments from surveys is no longer a manual nightmare. AI automatically categorizes responses, determines overall sentiment, identifies recurring themes, and spots hidden cues of demotivation or incipient conflicts. This provides structured analytics rather than a raw array of text.
- Predictive Analytics: Based on collected data, AI can predict the risk of voluntary turnover (“flight risk”), identify potential team conflicts, identify the best candidates for promotion, and even suggest when and in which department a staff increase is needed.
3. Training and Development
- Individual Educational Programs: AI personalizes the learning experience. Based on an analysis of current knowledge, education, and career goals, it forms a unique learning trajectory. If the goal is to become a leader, the emphasis will be on management; if an expert, then on specialized tech.
- Adaptive Skills Assessment: Instead of standard tests, AI uses adaptive systems that generate tasks in real-time, adjusting to the employee’s knowledge level. This allows for a deeper understanding of strengths and weaknesses.
- AI Assistants for Onboarding: Chatbots based on neural networks provide introductory training for newcomers, answer questions 24/7, and explain corporate processes—a massive benefit for distributed, global teams.
How to Relieve the HR Department: A Step-by-Step Implementation Plan
The introduction of AI is not a one-time event, but a process.
Step 1: Audit, Goal Setting, and Bottleneck Identification
Start with an in-depth analysis of current HR processes from hiring to dismissal. The goal is to record where the HR team spends the most manual labor on routine operations (e.g., initial screening, answering FAQs). Interview HR specialists to identify tasks that cause the most irritation. Formulate clear, measurable KPIs (e.g., “reduce recruitment time by 20%,” “increase candidate satisfaction by 15%”).
Step 2: Data Preparation and Structuring
The quality of AI work directly depends on the quality of data. Take inventory, collect, and structure all relevant HR data: resume databases, employee profiles, performance scores, and engagement data. Addressing security and data privacy (GDPR, CCPA) at this stage is critical.
Step 3: Selection and Pilot Implementation
Select AI tools that fit your needs and budget. Start with a single, controlled process, such as a chatbot for candidate FAQs. Be clear about the specific goal for this pilot to accurately assess its effectiveness later.
Step 4: Integration and Team Training
Integrate the solution and conduct a training program for HR specialists. Explain the capabilities and limitations of the new tool so the team views it as an assistant, not a threat. Adapt current HR processes to the new capabilities by reassigning responsibilities.
Step 5: Analysis, Scaling, and Ethical Audit
After the pilot, constantly monitor performance. Collect feedback from the team and candidates. Remember, AI can make mistakes, so the final decision should always remain with a human. Conduct ethical audits to eliminate bias. If the pilot is successful, scale it to other processes.
Step 6: Building a Data-Driven Culture
Don’t stop at one tool. Identify the next priority area. In the long term, drive the active use of data and analytics in all HR decisions to transform the department into a strategic business partner.
Popular Global AI Solutions for HR
The global HR Tech market is actively developing with solutions for every need:
- Eightfold AI: A talent intelligence platform that uses deep learning to match candidates to jobs and predict their potential for future roles, significantly aiding in retention and internal mobility.
- Paradox (Olivia): A conversational AI assistant that automates screening, scheduling, and candidate Q&A via mobile chat, used by major global retailers and hospitality chains.
- Workday HCM: A leading global enterprise suite that incorporates AI to analyze workforce skills, predict talent gaps, and automate financial and HR planning.
- HireVue: The global leader in video interviewing technology, using algorithms to evaluate candidates’ verbal and non-verbal cues to assess soft skills and cultural fit.
- Visier: A people analytics platform that uses AI to provide insights into workforce trends, diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) metrics, and turnover risks.
- ChatGPT Enterprise / Jasper: Generative AI tools widely used for drafting job descriptions, offer letters, internal communications, and interview scripts.
- DocuSign / PandaDoc: Platforms that automate the document lifecycle with AI elements, ensuring seamless, legally binding digital signatures for global hiring.
- HackerRank / CodeSignal: Platforms for automated technical screening of developers, using AI to detect plagiarism and evaluate code quality instantly.
- Otter.ai / Fireflies.ai: AI meeting assistants that transcribe interviews and meetings in real-time, summarizing key points and action items for recruiters.
Typical Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Despite all the benefits, AI adoption comes with risks:
- Low-quality data: “Dirty” or incomplete data leads to incorrect insights.
- Algorithm bias: AI can reinforce existing biases (e.g., favoring one demographic over another if historical hiring data reflects that bias). This is a major compliance risk.
- Inflated expectations: Underestimating AI “hallucinations” (erroneous information) can be dangerous in decision-making.
- Integration issues: Incompatibility with existing legacy systems creates extra costs and data silos.
- Lack of competencies: Lack of skills among HR specialists to work with AI tools negates the benefits.
- Privacy risks: Incorrect processing of personal data can lead to leaks and violations of laws like GDPR.
- Lack of human touch: Excessive automation can reduce employee loyalty.
How to minimize risks: Ensure data quality and relevance. Conduct regular ethical audits of algorithms. Clearly delineate areas of responsibility—humans must make the final call. Invest in HR training. Protect personal data by understanding where it is stored and if it is used to train models. Finally, maintain personal communication to preserve the human element.
Success Stories in Global Companies
Many multinational giants are already reaping the rewards of AI in HR:
- Hilton Hotels: By using AI for recruitment, Hilton reduced its hiring timeline from 6 weeks to just 5 days. The AI handled initial assessments and scheduling, improving the candidate experience significantly.
- Unilever: The consumer goods giant saved over 100,000 hours of recruitment time annually by using AI games and video interviews to screen entry-level candidates, simultaneously increasing the diversity of their hires.
- IBM: IBM uses its own Watson AI to predict employee flight risk with 95% accuracy, allowing managers to intervene and retain top talent before they resign. This reportedly saved the company nearly $300 million in retention costs.
- Accenture: Uses AI-driven learning platforms to offer personalized training recommendations to its massive global workforce, ensuring skills remain relevant in a changing market.
The Future of HR with AI
Experts agree that the future is a symbiosis of humans and machines. Key trends for the coming years include:
- Hyper-personalization: AI will allow companies to create unique career paths, training programs, and even benefits packages tailored to the individual needs of every employee.
- Predictive Analytics as Standard: Predicting turnover, burnout, and hiring needs will become a routine, proactive task rather than a reactive one.
- AI Agents: Instead of simple chatbots, full-fledged autonomous agents will appear. They will solve multi-step tasks, such as organizing the entire adaptation cycle for a new hire across multiple departments.
- Strengthened Ethics: As AI’s impact grows, transparency and fairness will become paramount, guided by emerging regulations like the EU AI Act.
Conclusion
The introduction of artificial intelligence into HR processes has ceased to be a matter of competitive advantage and has become a necessity for companies seeking to remain competitive in today’s global labor market. As the examples of industry leaders show, the competent use of AI allows you to optimize costs, increase efficiency, and drastically improve the employee experience.
However, successful implementation requires a balanced approach: a combination of technological capabilities with human expertise, attention to ethical aspects, and continuous development of HR specialists’ competencies. Artificial intelligence will not replace HR professionals, but it will become their reliable assistant in creating effective, adaptive, and human-centered organizations. The future belongs to companies that can harmoniously integrate the technological capabilities of AI with unique human qualities such as empathy, creativity, and strategic thinking.